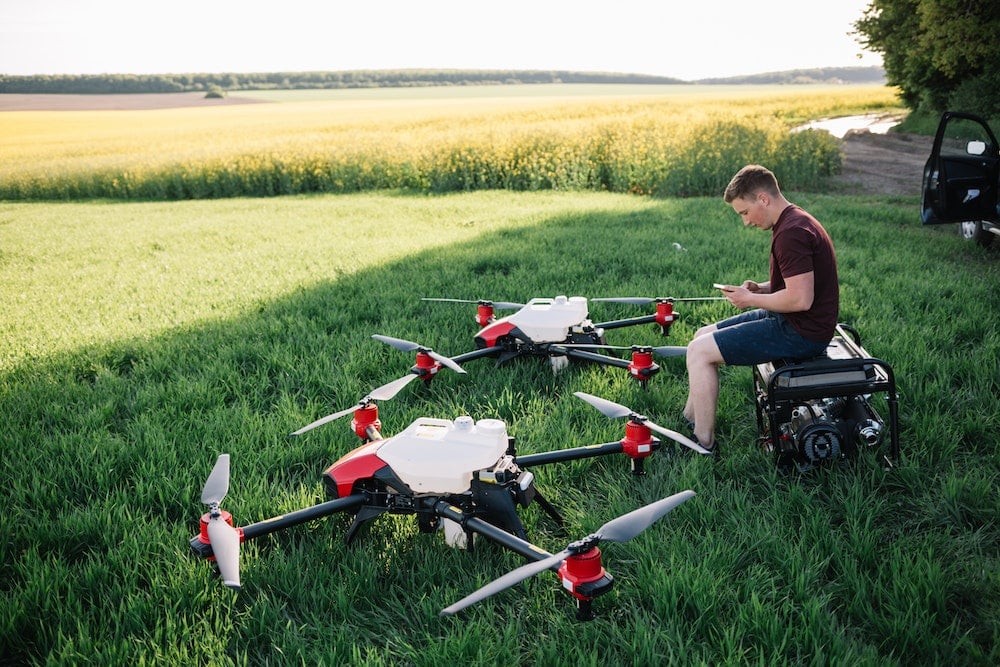
Agriculture has long been a cornerstone of economic activity in the UK, feeding the nation and contributing significantly to GDP. But as concerns over environmental impact and the overuse of pesticides heighten, it’s time for a shift. Advancements in technology offer a solution in the form of precision farming – a method that could significantly alter the UK agricultural landscape. In this article, we will delve into how precision farming can reduce pesticide use in UK agriculture, enhancing not only the productivity and sustainability of agricultural systems but also protecting our environment and health.
Precision Farming: An Overview
Precision farming, also known as precision agriculture, is a management approach that utilizes modern-day technology to monitor and manage agricultural operations. By integrating real-time data on various aspects of farming, such as soil conditions, crop health, weather data, and much more, precision agriculture enables farmers to make more informed decisions. This leads to optimized resource usage, improved productivity, and reduced environmental impact.
Dans le meme genre : How to Use Social Entrepreneurship to Address Homelessness in UK Cities?
The goal of precision farming is to ensure that the right amount of resources – be it water, fertilizer, or pesticides – is applied at the right time, in the right place, and in the right amount. This is achieved by utilizing a range of technologies, such as GPS, remote sensing, and data analytics, to gather and analyze data at an incredibly detailed level.
The Role Of Precision Farming In Pesticide Management
Pesticides play a crucial role in agricultural production. They help in controlling pests, diseases, and weeds that can adversely affect crop yield. However, the overuse of pesticides has been linked to a range of environmental and health problems. Precision farming provides a solution to this issue by enabling more efficient and targeted use of pesticides.
A voir aussi : What Are the Top Tips for Learning a New Language as an Adult in the UK?
Precision farming systems allow farmers to apply pesticides only where they are needed and in the exact quantities required. This is achieved through technology-based tools that map the field, identifying areas of pest infestation, and directing pesticide application accordingly. With this targeted approach, the overall amount of pesticides used can be drastically reduced, without compromising on crop yield.
Moreover, precision farming technologies can predict pest infestations based on past data and current weather conditions, allowing farmers to preventatively apply pesticides in a targeted manner. This proactive approach not only minimizes pesticide use but also prevents crop damage, maximizing yield.
The Impact Of Precision Soil Management
Soil is the foundation of any agricultural operation, and its management is crucial for sustainable farming. Precision farming technologies enable more effective soil management, influencing the use and impact of pesticides.
Precision soil management involves collecting data on soil characteristics, including nutrient content, moisture levels, and pH levels. This data is then used to create a detailed soil map of the field, allowing farmers to understand the specific needs of different areas.
By understanding the soil conditions in their fields, farmers can customize their pesticide application. For instance, if a particular area of the field has a high pest susceptibility due to poor soil health, farmers can apply pesticides only to that specific area, thus reducing overall pesticide usage. Additionally, healthier soil, achieved through precision management, can reduce a crop’s susceptibility to pests, further decreasing the need for pesticides.
Harnessing Data For Water-Based Applications
Water plays a major role in pesticide application. The amount of water available and its distribution can influence the effectiveness of pesticides and their environmental impact. Through precision farming, water management can be improved, reducing the need for pesticide use.
Precision farming technologies enable farmers to monitor the water status in their fields accurately. This information can be used to optimize irrigation schedules, improving water efficiency. When water is efficiently managed, crops are healthier and less susceptible to pests, reducing the need for pesticides.
Moreover, precision farming allows for water-based pesticide applications. In this method, pesticides are mixed with irrigation water and applied to crops. Because the application is more targeted, less pesticide can be used, further reducing the potential for environmental harm.
The Future Of UK Agriculture: Embracing Precision Technologies
While the promise of precision farming in reducing pesticide use is clear, the adoption of these technologies in the UK agriculture industry is still a work in progress. However, increased awareness about the benefits of precision agriculture, coupled with support from government and industry bodies, is gradually shifting the tide.
A key factor that is likely to drive the adoption of precision farming in the UK is its potential to increase productivity and profitability. By reducing resource wastage, improving crop yield, and minimizing environmental impact, precision farming can boost the bottom line for farmers. Also, as consumers become more conscious about the environmental impact of their food choices, farms that adopt sustainable practices are likely to gain a competitive edge.
In conclusion, precision farming offers a viable solution to the overuse of pesticides in UK agriculture. By embracing precision technologies, UK farmers can revolutionize their agricultural practices, improving productivity and sustainability while safeguarding the environment and public health.
The Potential of Variable Rate Technology
The concept of variable rate technology (VRT) is inherent to the success of precision farming. It helps farmers to make decisions that are data-driven and tailored to the specific needs of different areas within their fields. Through this technology, the application rate of pesticides can be varied according to the specific needs of different crop zones.
Variable rate technology uses a range of methods to gather data on fields. These include remote sensing technologies such as drones, satellites, and sensors installed directly in the field. These technologies collect real-time data on a range of factors including soil moisture, crop health, and weather conditions. This data is then analyzed and used to create a detailed map of the field, highlighting areas with different needs.
Using this map, farmers can program their machinery to apply pesticides at variable rates across the field. For instance, areas with high pest susceptibility can receive a higher dose of pesticides, while areas with low susceptibility can receive a lower dose. This targeted and data-driven approach ensures that pesticides are used only where they are needed, and in the right quantities, drastically reducing overall pesticide use.
Variable rate technology not only enhances crop management but also significantly reduces the environmental impact of farming operations. By minimizing unnecessary pesticide applications, VRT helps to protect biodiversity, preserve soil health, and prevent water contamination – all critical concerns in the face of climate change.
Guidance Systems and Control Systems in Precision Agriculture
Guidance systems and control systems are essential components of precision agriculture technologies. They facilitate real-time monitoring and efficient control of farming operations, enabling optimized use of resources, including pesticides.
Guidance systems, often GPS-based, allow for accurate navigation of agricultural machinery across the field. They ensure precise application of pesticides, reducing wastage and minimizing off-target effects. Guidance systems also enable farmers to work in lower visibility conditions, such as at night or in fog, further enhancing productivity.
Meanwhile, control systems regulate the functioning of farm machinery, including the amount and distribution of pesticides. Advanced control systems can automatically adjust the application rate of pesticides based on real-time data. For instance, if sensors detect an increase in pest activity in a certain area, the control system can increase the pesticide dose for that specific area.
By providing precise control over the application of pesticides, these systems play a crucial role in reducing pesticide use in precision farming. They ensure that pesticides are applied in an efficient and targeted manner, minimizing overuse and environmental harm.
Conclusion: The Way Forward
The adoption of precision farming in UK agriculture represents a step forward towards sustainable and productive farming practices. By integrating data analytics, variable rate technology, remote sensing, and advanced guidance and control systems, precision farming can significantly reduce the unnecessary use of pesticides.
Not only does precision farming offer a viable solution to the overuse of pesticides, but it also presents an opportunity for UK farmers to stay competitive in an increasingly environmentally-conscious market. By reducing their environmental impact, farmers can meet the demands of consumers seeking sustainably produced food.
Furthermore, with the challenges posed by climate change, these technologies offer a resilient solution. Precision agriculture enables farmers to adapt their practices in real time, enhancing their ability to respond to changing weather patterns and conditions.
In conclusion, the integration of precision farming into UK agriculture is a necessity. By harnessing the power of these advanced technologies, farmers can ensure sustainable and productive agricultural practices, safeguarding our environment and public health in the process.